Research Manual 5th Edition - Profession Analysis
Profession Analysis
RM5 has a worldwide profession database of 295 professions in the Team Management Profile Questionnaire sample. The distinction of what is coded as a profession and what is not, is drawn from whether a specific qualification must be obtained for a person to hold that position, i.e., doctor, lawyer/solicitor, forensic scientist, fire-fighter, or boilermaker. Analyses are available for the 135 professions where there are 100 or more respondents. Some key points worthy of comment are:
- The profession samples with the highest mean Extrovert score are Media/Public Relations Specialist (7.4) and Fundraiser (6.8).
- The profession samples with the highest mean Introvert score are Draftspersons (4.4) and Geographic Information Systems Specialists (3.6).
- The highest mean score for Creative information-gathering is 5.2 for Architects, followed by Psychologists and Multimedia Designers/Artists which both recorded 4.9.
- The profession samples with the highest mean score for Practical information-gathering are Paralegals (7.9) and Personal/Executive Assistants (7.5).
- The highest mean scores for Analytical decision-making are Geoscientists and Geophysicists (16.5).
- The highest mean score for Beliefs decision-making is 0.34 for Priests/Ministers of Religion/Pastors/Chaplains.
- The profession sample with the highest mean Structured score is 8.8 for Engineers: Industrial, very closely followed by Hospitality Workers at 8.6.
- The profession samples with the lowest mean Flexible score are Guidance/Career Counsellors (0.1) and Psychologists (0.2).
Percentile norms for all 135 Professions are available in RM5. You can use these tables to compare, for example, Geoscientists with the Priest/Minister of Religion/Pastor/Chaplain profession. At the mean sample score of A=16.5, 50% of Geoscientists have a higher score and 50% a lower score. Applying that mean score of A=16.5 to the Priest/Minister of Religion/Pastor/Chaplain percentile norms data shows that 94% of them have a lower Analytical score. This shows the significant difference between these two profession groups on the A-B scale. Similar comparisons can be made across the four scales for the 135 Professions.
Another way of interpreting the Profession database is by looking at the role preference distribution for each Profession. Below are a few interesting comparisons:
|
|
|
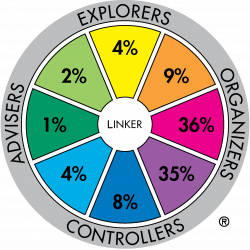
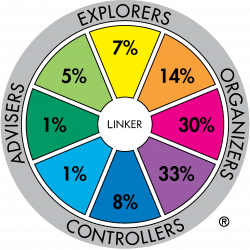
Major role preference distribution for profession sample: Armed Forces - NCO (n=138) |
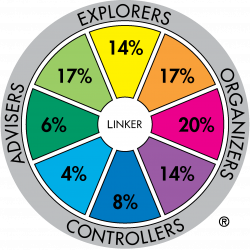
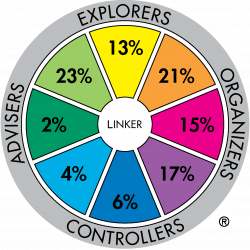
Major role preference distribution for profession sample: Arts & Media Professionals (n=360) |
The difference between these two profession groups is very significant. For example 37% of the Arts and Media sample have major role preferences in the Adviser-Explorer part of the Wheel whereas the Armed Forces:NCO sample has 7% in the same sectors.
|
|
|
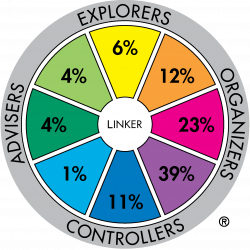
Major role preference distribution for profession sample: Paralegal (n=119) |
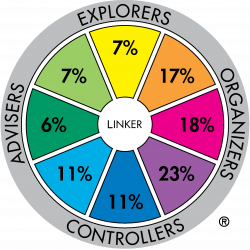
Major role preference distribution for profession sample: Aged/Disability Care Worker (n=113) |
Significant differences also occur between the Para-legal and Aged/Disability Care Worker samples. Here the Upholder-Maintainer sector is 11 times that of the Para-legal sample. Of the 135 Profession samples reported, the para-legal sample has the highest representation of Concluder-Producers (39%).
|
|
|
Major role preference distribution for profession sample: Accountant (n=12,153) |
Major role preference distribution managers working in R&D at Hewlett Packard Laboratories (%) (n=132) |
The data for the Accountant profession show a strong representation in the Thruster-Organiser and Concluder-Producer sectors. Interesting data is also highlighted in a sample of 132 professionals working in the Palo Alto R&D Department of Hewlett-Packard where I ran a number of workshops earlier in my career. Here 23% of respondents were in the Creator-Innovator sector compared with only 17% in the Concluder-Producer sector. Interestingly, many of these employees had a spilt Wheel between the Creator-Innovator and Thruster-Organiser sectors.
The Profession data analyses are another ‘brick in the wall’ for the many criterion-related validity studies reported in RM5. Most of the 135 Profession data sets show a relationship between role preference and the Type of Work which is important in carrying out that job function. Two factors are at work here. People are definitely attracted to jobs that provide an overlap with their preferences. But over time, the job demands can have a substantial influence in changing people’s work preference, particularly as they develop new skills and grow in the job. A two-thirds overlap between preferences and work seems to be an ideal goal.
References:
- McCann, D.J., & Mead, N.H.S., (Eds.), (2018), Team Management Systems Research Manual: 5th Edition, Team Management Systems, Brisbane, and York.
Copyright © Institute of Team Management Studies. All rights reserved.